Thymectomy
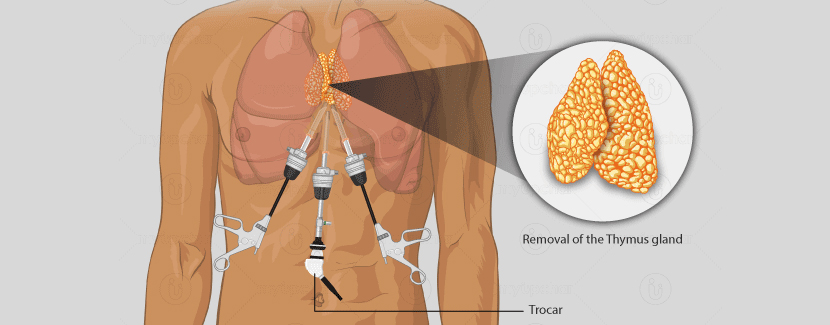
Thymectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of the thymus gland. The thymus gland is located in the upper chest and is an important part of the immune system, playing a role in the development and maturation of T-cells.
Thymectomy may be performed for a variety of reasons, including the treatment of thymoma (a type of tumor that originates in the thymus gland), myasthenia gravis (an autoimmune disorder that affects the neuromuscular junction), and other autoimmune diseases such as lupus and rheumatoid arthritis.
There are two main types of thymectomy: open thymectomy and minimally invasive thymectomy. Open thymectomy involves making a large incision in the chest, while minimally invasive thymectomy may be performed using video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) or robotic surgery. Minimally invasive thymectomy tends to result in less pain and a quicker recovery time than open thymectomy.
Thymectomy is generally considered a safe and effective procedure, but as with any surgery, there are risks and potential complications, including bleeding, infection, damage to surrounding organs, and anesthesia-related complications. It's important to discuss the risks and benefits of thymectomy with a qualified healthcare provider to determine if it is the right treatment option for you.










