Laparoscopic Adrenalectomy
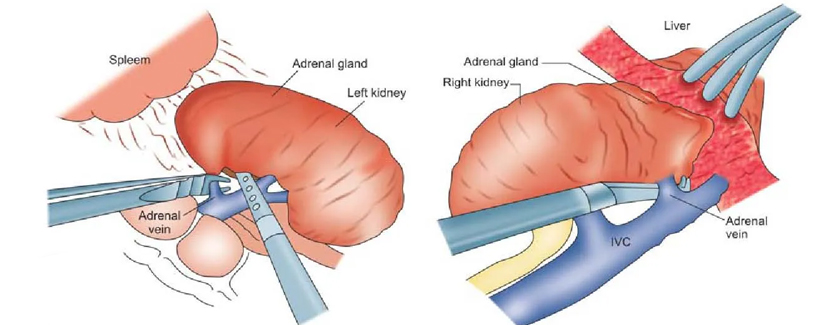
Laparoscopic adrenalectomy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure to remove one or both adrenal glands. The adrenal glands are located above the kidneys and produce hormones that regulate various bodily functions, including blood pressure, metabolism, and response to stress.
During laparoscopic adrenalectomy, small incisions are made in the abdomen and a laparoscope (a thin, flexible tube with a camera) and surgical instruments are inserted through the incisions. The surgeon uses the laparoscope to visualize the adrenal gland and surrounding tissues, and the instruments to carefully remove the gland.
Compared to traditional open surgery, laparoscopic adrenalectomy offers several advantages, including shorter hospital stays, faster recovery times, and less postoperative pain. It is generally considered a safe and effective treatment option for various adrenal gland conditions, including tumors, hyperplasia, and hypersecretion syndromes.
However, laparoscopic adrenalectomy is not suitable for all patients, and potential risks and complications should be discussed with a qualified healthcare provider.










