Laparoscopic Hepatic Resection
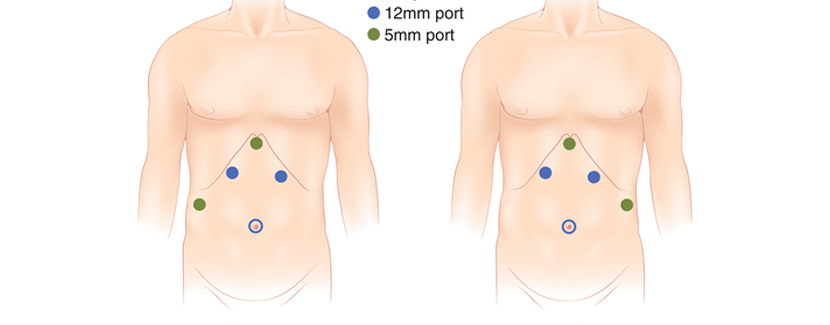
Laparoscopic hepatic resection is a minimally invasive surgical technique that involves removing a part of the liver through small incisions in the abdomen using a laparoscope, which is a long, thin instrument with a small video camera and light source attached to it. The liver is a vital organ that plays a crucial role in the metabolism, detoxification, and storage of nutrients. Hepatic resection is a surgical procedure used to remove a part of the liver affected by cancer, cysts, or other diseases.
The advantages of laparoscopic hepatic resection over traditional open surgery include smaller incisions, less pain, less blood loss, shorter hospital stay, and faster recovery. However, the technique requires a skilled surgeon with experience in laparoscopic surgery and specialized equipment.
The procedure begins with the insertion of a laparoscope and other specialized instruments through small incisions in the abdomen. The surgeon then carefully dissects and removes the affected part of the liver, which is usually done with the help of a specialized surgical stapler that seals blood vessels and bile ducts. After the liver is removed, the surgeon will close the incisions with sutures or surgical glue.
Laparoscopic hepatic resection is generally considered safe and effective, but like any surgical procedure, it carries some risks, such as bleeding, infection, and damage to surrounding organs. Patients who undergo laparoscopic hepatic resection usually require close follow-up care to monitor for any complications and ensure a full recovery.










